Local Plan 2011-2031 Proposed Submission Draft
APPENDICES
Appendix 1: Superseded Policies
The schedule below is taken from the Local Development Scheme, January 2016 and sets out how, where and when (if appropriate) policies within the saved District Local Plan No. 2 with Alterations (1996) will be replaced. Those policies which were not saved by the Secretary of State in September 2007 do not appear in the schedule.
|
District Local Plan No.2 with Alterations To be replaced |
Replacement Policy contained in the North Hertfordshire Local Plan 2011 – 2031 |
||
|
Policy 2 |
Green Belt |
Policy SP5 |
Countryside and Green Belt |
|
Policy 3 |
Settlements within the Green Belt |
Policy SP2 |
Settlement hierarchy |
|
Policy 4 |
North East Stevenage |
Not applicable |
|
|
Policy 5 |
Excluded villages |
Policy SP2 |
Settlement hierarchy |
|
Policy 6 |
Rural area beyond the Green Belt |
Policy CGB1 |
Rural areas beyond the Green Belt |
|
Policy 7 |
Selected villages beyond the Green Belt |
Policy SP2 Policy D1 |
Settlement hierarchy Sustainable design |
|
Policy 8 |
Development in towns |
Policy SP2 |
Settlement hierarchy |
|
Policy 9 |
Royston's development limits |
Policy SP2 Policy CGB1 Policy CGB5 |
Settlement hierarchy Rural areas beyond the Green Belt Urban Open Land |
|
Policy 11 |
Chilterns Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty |
Policy NE3 |
The Chilterns Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB) |
|
Policy 14 |
Nature conservation |
Policy NE5 Policy NE6 |
New and improved public open space and biodiversity Designated biodiversity and geological sites |
|
Policy 16 |
Areas of archaeological significance and other archaeological areas |
Policy HE4 |
Archaeology |
|
Policy 19 |
Historic parks and gardens |
Policy HE1 |
Designated heritage assets |
|
Policy 21 |
Landscape and open space patterns in towns |
Policy NE4 |
Protecting open space |
|
Policy 25 |
Re-use of rural buildings |
Policy CGB4 |
Existing rural buildings |
|
Policy 26 |
Housing proposals |
Policy SP8 Policy HS1 |
Housing Local housing allocations |
|
Policy 28 |
House extensions |
Policy D2 |
House extensions, replacement dwellings and outbuildings |
|
Policy 29 |
Rural housing needs |
Policy CGB2 |
Exception sites in rural areas |
|
Policy 29A |
Affordable housing for urban local needs |
Policy HS2 |
Affordable housing |
|
Policy 30 |
Replacement or extension of dwellings in the countryside |
Policy CGB4 Policy D2 |
Existing rural buildings House extensions, replacement dwellings and outbuildings |
|
Policy 33 |
Relatives and staff accommodation |
Policy CGB3 Policy D2 |
Rural workers dwellings House extensions, replacement dwellings and outbuildings |
|
Policy 34 |
Residential caravans and mobile homes |
No replacement policy |
|
|
Policy 36 |
Employment provision |
Policy SP3 Policy ETC1 |
Employment Appropriate uses in employment areas |
|
Policy 37 |
Business uses (B1 Use Class) |
Policy SP3 Policy ETC1 |
Employment Appropriate uses in employment areas |
|
Policy 39 |
Leisure uses |
Policy ETC3 |
New retail, leisure and other main town centre development |
|
Policy 42 |
Shopping |
Policy SP4 Policy ETC3 |
Town and Local Centres New retail, leisure and other main town centre development |
|
Policy 43 |
Shopping areas in town centres |
Policy ETC4 Policy ETC5 |
Primary shopping frontages Secondary shopping frontages |
|
Policy 45 |
Shopfronts |
Policy D1 |
Sustainable design |
|
Policy 47 |
General aviation |
No replacement policy |
|
|
Policy 51 |
Development effects and planning gain |
Policy SP7 |
Infrastructure requirements and developer contributions |
|
Policy 55 |
Car parking standards |
Policy T2 |
Parking |
|
Policy 57 |
Residential guidelines and standards |
Policy SP9 Policy D1 |
Design and sustainability Sustainable design |
|
Policy 58 |
Letchworth Garden City design principles |
Policy SP13 Policy SP15 Policy D1 |
Historic Environment North of Letchworth Garden City Sustainable design |
Appendix 2: Local Plan Designations
The Local Plan Proposals Map includes the following designations, which are set by, and specifically relate to, policies in the Plan:
- Green Belt
- Rural Area Beyond the Green Belt
- Urban Open Land
- Business Areas
- Employment Areas
- Employment Sites
- Housing Sites
- Neighbourhood Centres
- Settlement Boundaries
- Town Centre Boundaries
- Primary Shopping Frontage
- Secondary Shopping Frontages
- Mixed use Allocations
- Safeguarded Land
- Gypsy / Traveller Site
The Proposals Map also includes the following designations, which although referred to by policies in the Plan, are not the responsibility of the Local Plan and the extents of the designations are not set by the Local Plan process. The relevant authority listed next to the allocation (below) is responsible for their designation. Their extents may change throughout the duration of the Local Plan and so viewing the organisations websites is recommended for the most up-to-date position (In the case of Conservation Areas, whilst the local authority is responsible for setting their extent it is a separate process to the Local Plan):
|
Designation |
Designating authority |
|
Sites of Special Scientific Interest |
Natural England |
|
Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty |
Natural England |
|
Conservation Areas |
North Hertfordshire District Council |
Additionally there are a number of other designations which policies in the Local Plan refer to; however, as the Local Plan does not control their designation or set their extents and they are so numerous and extensive that they would confuse the other designations, they are not included on the Proposals Map. Again the authority listed next to the allocation is responsible for their designation and so viewing the organisations websites is recommended for the most up-to-date position (again, in the case of designations that are the responsibility of the District Council the process for setting their extents is separate to the Local Plan).
|
Designation |
Designating authority |
|
Flood Risk |
Environment Agency |
|
County Wildlife Sites |
Herts and Middlesex Wildlife Trust / Natural England / Hertfordshire County Council |
|
Local Nature Reserves |
North Hertfordshire District Council / Herts and Middlesex Wildlife Trust |
|
Scheduled Ancient Monuments |
Historic England |
|
Archaeological Areas |
Historic England |
|
Listed Buildings |
Historic England |
|
Air Quality Management Areas |
North Hertfordshire District Council |
|
Contaminated land |
North Hertfordshire District Council |
|
Waste Site Allocations |
Hertfordshire County Council |
|
Minerals Site Allocations |
Hertfordshire County Council |
ALL LAYERS CAN BE VIEWED USING THE COUNCIL INTERACTIVE ONLINE MAPPING SYSTEM.
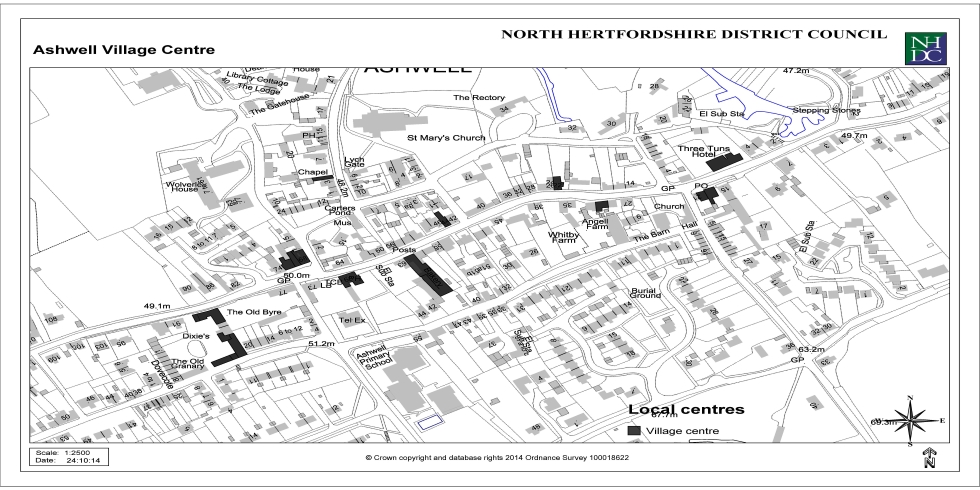
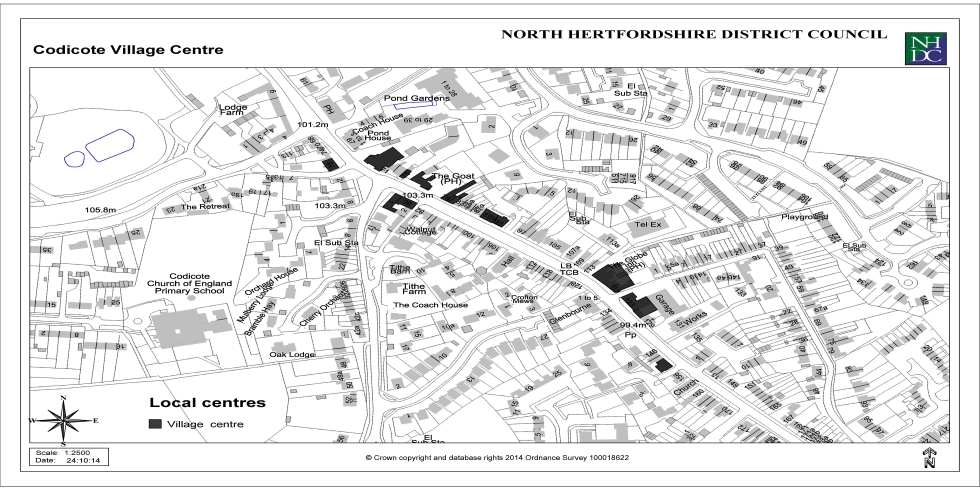
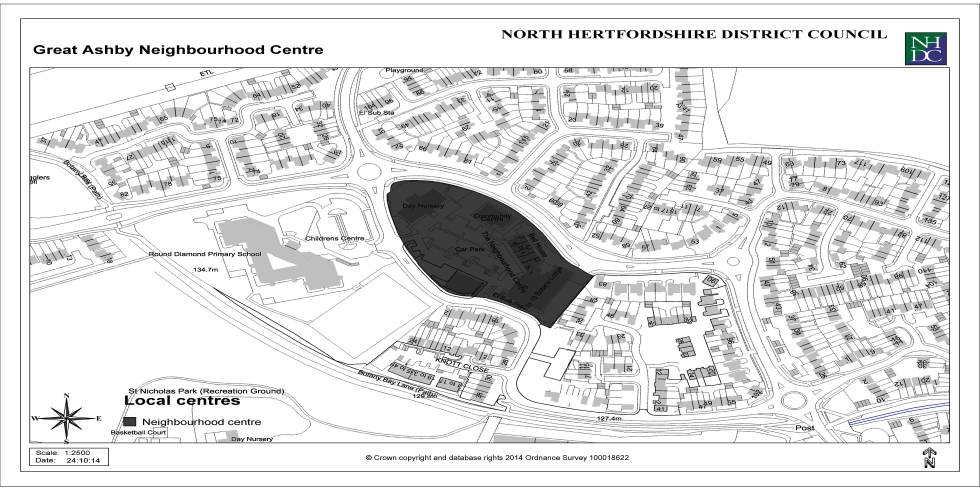
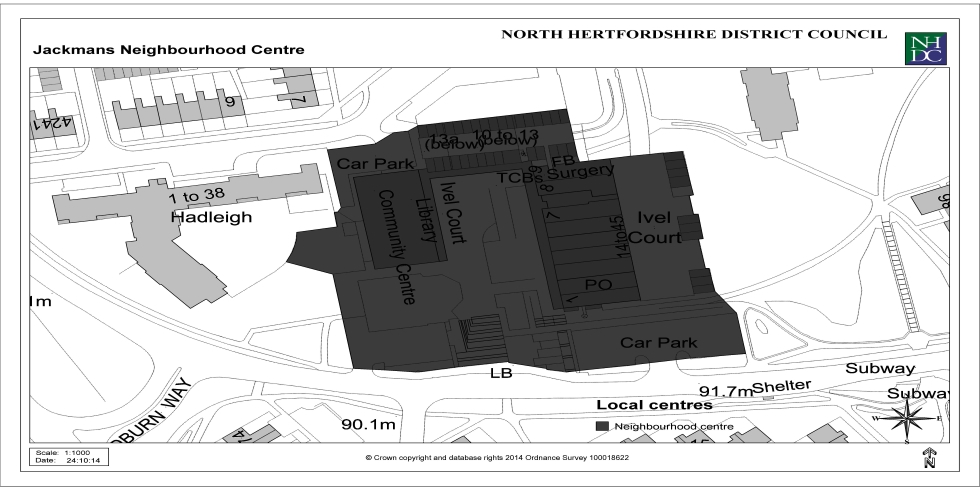
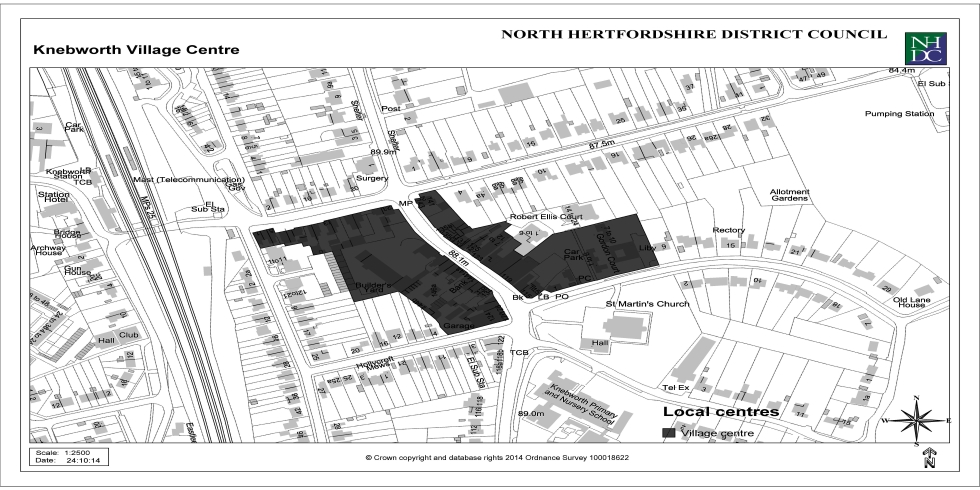
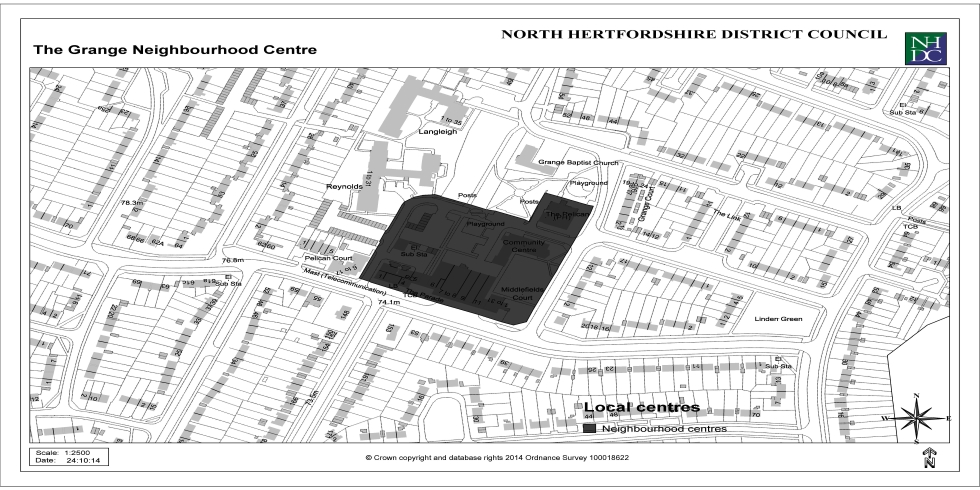
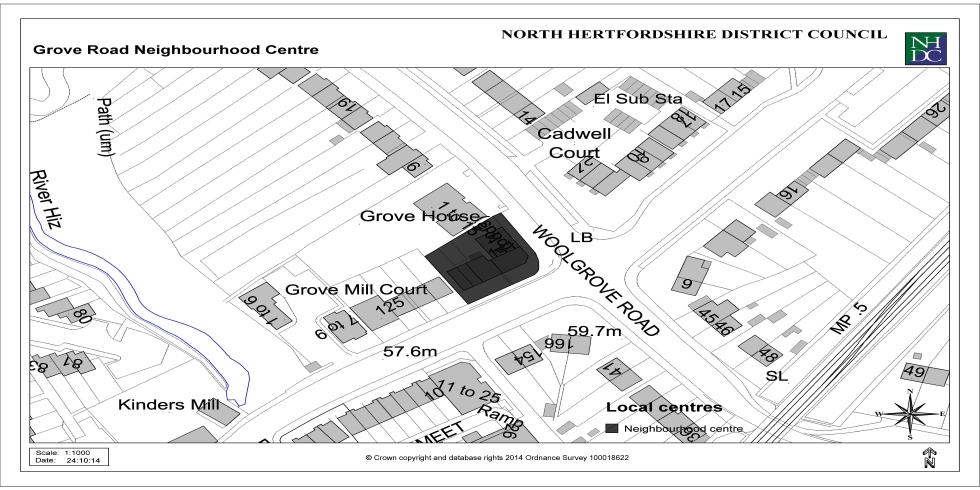
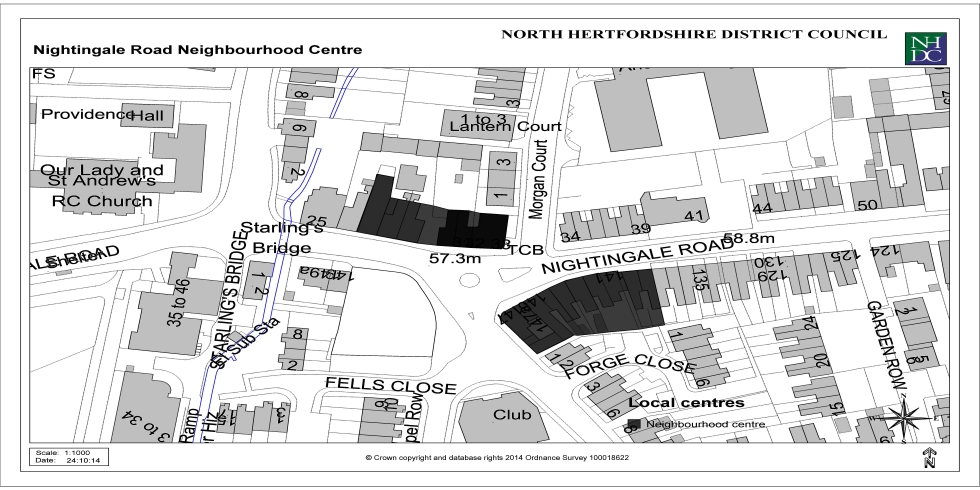
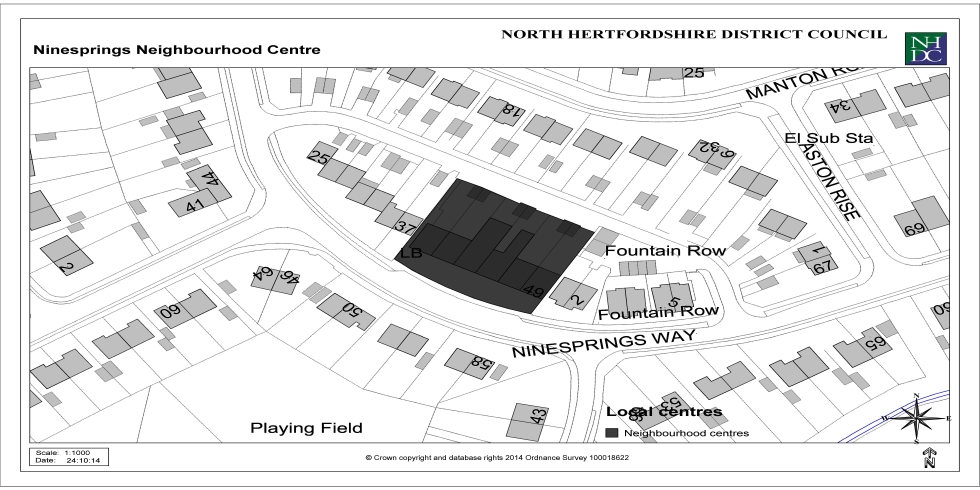
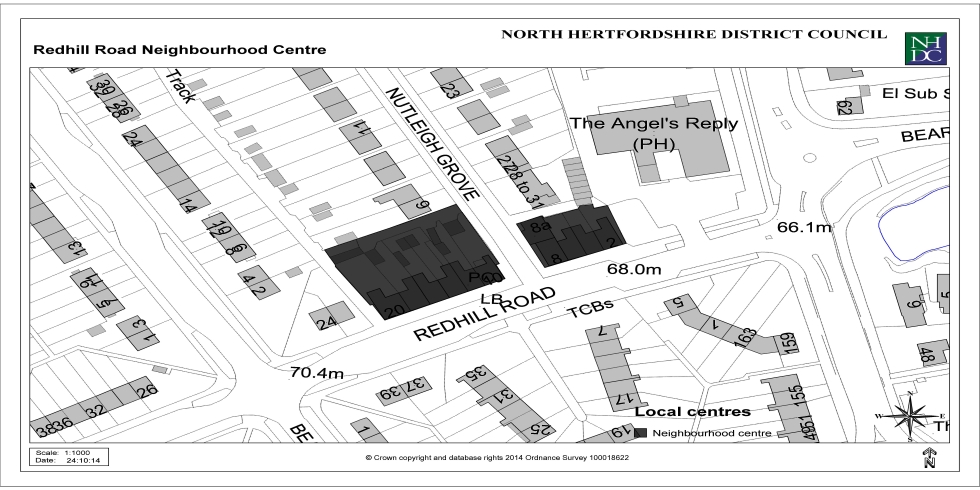
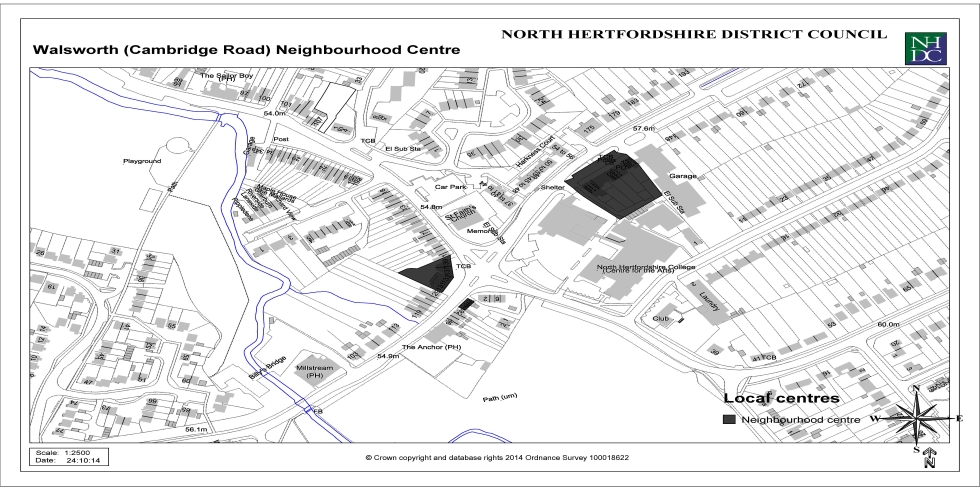
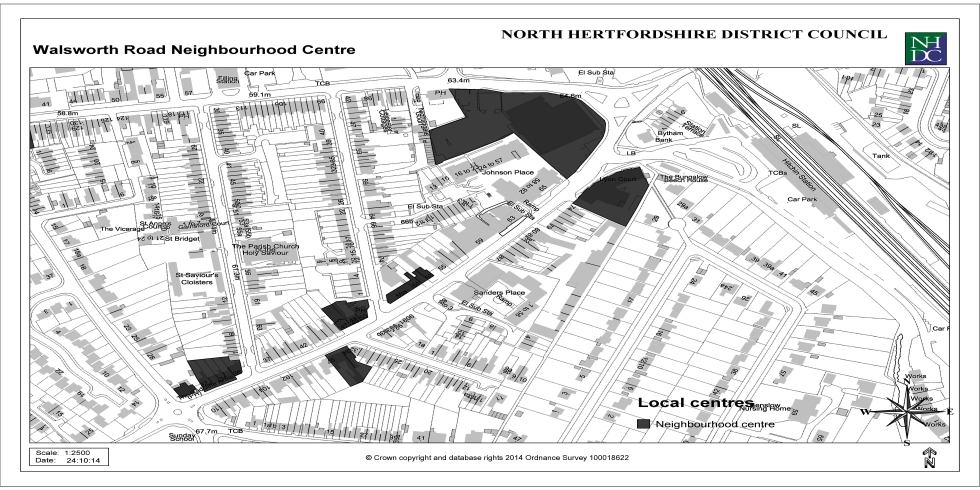
Appendix 3: Local Centres
Appendix 4: Car Parking Standards
Residential Parking Standards
|
Class Use C3 |
Car Parking Standard |
Minimum Cycle Parking Standard |
|
1 bedroom |
1 space per dwelling minimum |
1 secure covered space per dwelling. None if garage or secure area provided within curtilage of dwelling |
|
2+ bedrooms |
2 spaces per dwelling minimum |
The above standard will also require visitor / unallocated parking as set out below to be added. Garages will be counted towards meeting the standards only if they are at least 7m x 3m measured internally. Reductions will be considered only in exceptional circumstances e.g in town centres or other accessible locations with the availability of a range of local services and good local sustainable transport options and for e.g. small-scale conversion of buildings for a small number of residential units in defined town centres
|
Retirement developments (e.g. warden assisted independent living accommodation) |
1 space per dwelling minimum |
1 space per 8 units (visitors) |
|
Visitor / unallocated |
Between 0.25 and 0.75 spaces per dwelling (rounded up to nearest whole number) with the lower standard being applied where there are no garages in the schemes and the higher standard applied where every dwelling in the scheme is to be provided with a garage |
If no garage or secure area is provided within curtilage of dwelling then 1 covered and secure space per dwelling in a communal area for residents plus 1 space per dwelling for visitors |
For the above two standards, reductions in provision will be considered where
- Alternative publicly available off-street parking is available within 2 minutes walk of the site
- Visitor parking arising from small-scale (i.e. infill) development can be accommodated on-street without compromising highway safety, the amenity of existing residents or the ability for businesses to operate; or
Relevant evidence is submitted by the applicant which supports a reduction in standard and considers existing and future car ownership and likely visitor
Glossary
Adoption
Confirmation, usually by a legal notice in a newspaper, stating the final adoption of a planning policy document by a Local Planning Authority.
Affordable Housing
Social rented, affordable rented and intermediate housing for specified eligible households whose needs are not met by the market and which seeks to meet the needs of current and future eligible households at a cost low enough for them to afford.
Allocated Site/Site Allocation
Sites which are identified for a specific use e.g. housing or Green Belt on the Local Plan Policies Map.
Biodiversity
The variety of life in all forms (e.g. wildlife, plants etc).
Biodiversity Action Plan (BAP)
An overarching framework for habitat and species conservation, which works on the basis of partnership to identify local priorities and targets.
Brownfield site/Previously Developed Land (PDL)
Land which is or was occupied by a permanent structure, including the curtilage of the developed land (although it should not be assumed that the whole of the curtilage should be developed) and any associated fixed surface infrastructure. This excludes: land that is or has been occupied by agricultural or forestry buildings; land that has been developed for minerals extraction or waste disposal by landfill purposes where provision for restoration has been made through development control procedures; land in built-up areas such as private residential gardens, parks, recreation grounds and allotments; and land that was previously-developed but where the remains of the permanent structure or fixed surface structure have blended into the landscape in the process of time.
Buildings of Local Interest
Buildings designated by the local planning authority to be of local significance and included in a local list. Although they are not statutorily protected, close scrutiny will be given to any development affecting them.
Community Infrastructure Levy (CIL)
A levy allowing local authorities to raise funds from owners or developers of land undertaking new building projects in their area. The CIL must be collected through the preparation of a Charging Schedule, supported by a range of infrastructure planning and economic viability evidence.
Communities and Local Government, Department for (DCLG or CLG)
The government department which sets policy on local government, housing, urban regeneration, planning and fire and rescue. DCLG also has responsibility for all race equality and community cohesion related issues in England, and for building regulations, fire safety and some housing issues in England and Wales.
Comparison Goods/Convenience Goods
Comparison goods include clothing, shoes, household appliances, books, etc, where the customer can make a comparison between different retailers. This differs from convenience goods, which include everyday items such as food and drink.
Conservation Area
An area defined in the Planning (Listed Buildings and Conservation Areas) Act 1990 as 'an area of special architectural and historic interest, the character or appearance of which it is desirable to preserve or enhance.' Councils must publish a map showing the boundaries of these areas where extra planning controls apply and also produce a conservation area proposals statement.
Deliverable Site
To be considered deliverable for housing development, sites should:
- Be available now;
- Offer a suitable location for development now and contribute to the creation of sustainable, mixed communities; and
- Have a reasonable prospect that housing will be delivered on the site within five years.
Density
A measurement of how intensively land is occupied by built development. For housing, this is measured in dwellings per hectare (dpha).
Design and Access Statement
A document that explains the design concepts, implications and justification associated with a planning application. This includes how an applicant has carefully considered how everyone, including disabled people, older people and young children, will be able to use the development.
Developer Contribution
In-kind or financial contributions provided by developers to contribute to the cost of infrastructure and other items, in order that the development is acceptable in planning terms and accords with the policies in the Local Plan. This can take the form of a legal agreement or the operation of a tariff-based system for contributions. Legal agreements may take the form of a 'planning obligation', which is a legally enforceable obligation entered into under section 106 of the Town and Country Planning Act 1990 to mitigate the impacts of a development proposal.
Development Plan
Local Plans and Neighbourhood Plans, which have been adopted or made under powers in the Planning and Compulsory Purchase Act 2004, as amended by the Localism Act 2011.
Development Plan Document (DPD)
Planning policy documents which carry the most weight in a Local Plan. Once they have been prepared they have to be submitted to the Secretary of State at the Department of Communities and Local Government. They are then examined by an independent planning inspector to make sure that they meet legislative, regulatory and national policy requirements.
Development Management
The process by which proposals for new development are assessed by the Local Planning Authority. This is undertaken primarily through the determination of planning applications.
Evidence Base
The range of reports, studies, data and surveys specifically collected and used to inform Local Plan preparation.
Green Belt
Designated land – primarily open land – around built-up areas designed to limit urban sprawl and to define town and country areas. It is generally protected land with a strong presumption against development.
Green Infrastructure (GI)
A concept recognising the environmental, social and economic, often multi-functional value of the network of natural environmental components and green and blue spaces that lies within and between towns and villages. In the same way that the transport infrastructure is made up of a network of roads, railways and airports, etc. Green Infrastructure has its own physical components, including parks, rivers, street trees and moorland.
Greenfield Sites
Greenfield sites are land which is not previously developed and can include agricultural land in rural areas, but also undeveloped land within the urban area.
Index of Multiple Deprivation (IMD)
Published by the Government, and provides an overall measure of 'deprivation' across a range of indicators, against which social and economic conditions in one area can be compared to other areas in England.
Infrastructure Delivery Plan (IDP)
Supporting the Core Strategy and the wider Local Plan, this will set out the range of existing, planned and required infrastructure within the local authority area. This will identify standards of provision which should be adhered to, and set out the key infrastructure projects which will be critical to the successful delivery of the Local Plan.
Listed Buildings
Buildings or other built structures included in the statutory list of buildings of special architectural or historic interest of national significance. Listing decisions are made by the Secretary of State for Culture, Media and Sport and the listing system is administered by English Heritage.
Local Development Document (LDD)
A collective term for planning policy documents, including all parts of the Local Plan, Neighbourhood Plans and Supplementary Planning Documents.
Local Development Framework (LDF)
The term previously used to refer to the portfolio of Local Development Documents, including Development Plan Documents, Supplementary Planning Documents and various process documents. This term has been replaced with the term Local Plan, although this refers only to the portfolio of Development Plan Documents.
Local Development Scheme (LDS)
The business plan for production of the Local Plan. It identifies and describes the Development Plan Documents and when they will be produced. It covers a three-year period and is subject to updating following production of Monitoring Reports to check progress.
Local Enterprise Partnership (LEP)
A body designated by the Secretary of State for Communities and Local Government to create or improve the conditions for economic growth in an area.
Local Nature Partnership (LNP)
A body designated by the Secretary of State for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs to protect and improve the natural environment in an area and the benefits derived from it.
Local Nature Reserve (LNR)
A statutory designation made by local authorities (under the National Parks and Access to the Countryside Act 1949) relating to places with wildlife or geological features that are of special interest locally. LNRs are designated to support biodiversity and geodiversity, and offer opportunities for people to learn about and enjoy the natural environment.
Local Plan (LP)
The plan for the future development of the local area, drawn up by the local planning authority in consultation with the community.
Local Transport Plan (LTP)
A plan which sets out sub-regional objectives, strategies and policies for transport, detailing the schemes and initiatives that will be delivered, together with the performance indicators and targets used to monitor progress.
Local Wildlife Site (LWS)/Local Geological Site (LGS)
Previously known as Sites of Importance for Nature Conservation (SINC), or alternatively Site of Biological Interest (SBI)/Site of Geological Interest (SGI), these are areas of land with significant wildlife or geological value. Typically they can comprise an area of woodland, grassland meadows or a local water body.
Localism Act
Enacted in late 2011, the Act contains a wide range of legislative changes, including many affecting local authorities and local spatial planning. The Act introduced the legislative basis for: the abolition of Regional Strategies; a new 'duty to co-operate'; changes to the Community Infrastructure Levy (CIL) system; and neighbourhood planning. Further details are available on the DCLG website.
Main Town Centre Uses
Retail development (including warehouse clubs and factory outlet centres), leisure, entertainment facilities, intensive sport and recreation uses (including cinemas, restaurants, drive-through restaurants, bars and pubs, night-clubs, casinos, health and fitness centres, indoor bowling centres, and bingo halls), offices, and arts, culture and tourism development (including theatres, museums, galleries and concert halls, hotels and conference facilities).
Major Development
Defined in the Town and Country Planning (Development Management Procedure) (England) Order 2015 as:
development involving any one or more of the following-
(a) the winning and working of minerals or the use of land for mineral-working deposits;
(b) waste development;
(c) the provision of dwellinghouses where-
(i) the number of dwellinghouses to be provided is 10 or more; or
(ii) the development is to be carried out on a site having an area of 0.5 hectares or more
and it is not known whether the development falls within sub-paragraph (c)(i);
(d) the provision of a building or buildings where the floor space to be created by the
development is 1,000 square metres or more; or
(e) development carried out on a site having an area of 1 hectare or more.
Masterplan
An outline of the vision for the development of an area indicating the broad principles which should be followed in its development.
National Planning Policy Framework (NPPF)
Introduced by the Government in 2012, this replaced the majority of adopted national planning policy, including most Planning Policy Statements and Planning Policy Guidance notes. The NPPF is supplemented by remaining guidance, and a number of other policy statements. The NPPF sets out national priorities for delivering sustainable development and economic growth, including a very wide range of policies and guidance, relating to themes such as housing, environment and economy, and procedural matters (such as plan-making and decision-taking).
Neighbourhood Plan
A plan prepared by a Parish Council or Neighbourhood Forum for a particular neighbourhood (made under the Planning and Compulsory Purchase Act 2004 as amended by the Localism Act 2011). A neighbourhood plan would, once brought into effect, comprise part of the statutory Development Plan for the area. It would therefore, alongside any adopted Local Plan documents, need to be considered when assessing any development proposals affecting the area.
Plan Period
Refers to the time period of operation for a Local Plan.
Planning and Compulsory Purchase Act 2004
This Act made provision relating to spatial development and town and country planning, and the compulsory acquisition of land. It introduced the Local Development Framework (LDF) system for planning policy, and remains the main legislative basis for production of Local Plans.
Planning Condition
A condition imposed on a grant of planning permission (in accordance with the Town and Country Planning Act 1990) or a condition included in a Local Development Order or Neighbourhood Development Order.
Preferred Options Report
Refers to a stage in the preparation of a Local Plan document, involving consultation on a set of preferred policy options.
Previously Developed Land (PDL)
See entry for 'Brownfield site'.
Registered Provider (of Social Housing)
Independent, not-for-profit private sector organisations providing social housing. They are the UK's major provider of homes for rent, as well as providing opportunities for shared ownership. They were previously also known as 'Registered Social Landlords' or 'Housing Associations'.
Renewable and low carbon energy
Includes energy for heating and cooling as well as generating electricity. Renewable energy covers those energy flows that occur naturally and repeatedly in the environment – from the wind, the fall of water, the movement of the oceans, the sun and from biomass and deep geothermal heat. Low carbon technologies are those that can help reduce emissions (compared to conventional use of fossil fuels).
Scheduled Monument
A nationally important historic building or structure or archaeological site, given protection against detrimental and unauthorised change. When designated, Scheduled Monuments are added to the schedule (which has been kept since 1882) of monuments whose preservation is given priority over other land uses. Scheduled Monuments are also sometimes referred to as 'Scheduled Ancient Monuments'.
Shared Ownership
An arrangement where the ownership of a property is shared, usually between a Registered Social Landlord (RSL) and a private purchaser.
Special Protection Areas (SPA)
Protected sites designated in the UK under the Birds Directive (2009/147/EC codified from 79/409/EEC).
Statement of Community Involvement (SCI)
Sets out how the Council will consult and engage with the community and other stakeholders in the production of all documents within the Local Plan, and when determining planning applications.
Strategic Environmental Assessment (SEA)
European Directive 2001/42/EC (the SEA Directive) requires a formal environmental assessment of certain plans and programmes which are likely to have significant effects on the environment, known as Strategic Environmental Assessment. To meet the requirements of the directive, a body must prepare an environmental report in which the likely significant effects on the environment of implementing the plan or programme, and reasonable alternatives taking into account the objectives and geographical scope of the plan, are identified, described and evaluated.
Strategic Flood Risk Assessment (SFRA)
A document which is normally produced by a local planning authority in consultation with the Environment Agency, and which forms the basis for preparing appropriate policies for flood risk management at the local level.
Strategic Housing Land Availability Assessment (SHLAA)
A systematic assessment of the availability of land which is developable and deliverable for new housing within an area. The assessment includes a 'Call for Sites' where the public can promote sites as being suitable for housing development and an appraisal of deliverability by a panel of developers and Registered Social Landlords active in the local market.
Strategic Housing Market Assessment (SHMA)
A study across an identified largely 'self contained' housing market to assess how the market operates and is likely to operate in the future. A SHMA assesses past, current and future trends in housing type and tenure, household size, and housing need, and of the housing needs of specific groups with particular requirements. It is important to engage sub-regional partners and other key stakeholders involved in the local housing market when preparing a SHMA.
Supplementary Planning Document (SPD)
A planning policy document which provides supplementary information in respect of the policies contained in the Local Plan, and which focus on particular issues or places. They are subject to consultation, but are not subject to an independent examination.
Sustainability Appraisal (SA)
An assessment of the economic, environmental and social effects of a plan from the outset of the preparation process to allow decisions to be made that accord with sustainable development.
Sustainable Drainage Systems (SuDS)
These systems provide an alternative to the traditional methods of dealing with water drainage, aiming to mimic the natural movement of water from a development, slowing run-off, reducing flood risk, improving water quality and potentially providing attractive features.
Transport Assessment (TA)
A comprehensive and systematic process that sets out transport issues relating to a proposed development. It identifies what measures will be required to improve accessibility and safety for all modes of travel, particularly for alternatives to the car such as walking, cycling and public transport and what measures will need to be taken to deal with the anticipated transport impacts of the development.
Obe Travel Plan
A long-term management strategy for an organisation or site that seeks to deliver sustainable transport objectives through action which is articulated in a document that is regularly reviewed.
Use Classes Order
The Town and Country Planning (Use Classes) Order 1987 and subsequent amendments, group a number of land uses into categories or 'Use Classes'. Changes of use within the same Use Class or between certain different Use Classes as set out in the General Permitted Development Order (GPDO) are normally deemed to have consent and do not in most cases require specific planning permission.
Vitality and Viability (Town Centres)
Terms used to assess the health of a town centre or other centre as measured by a number of indicators, such as the overall floorspace for retail and leisure, diversity of uses, range of goods that are sold, retailer representation, expenditure retention, rental values, level of vacancies, pedestrian 'footfall' figures, etc.